
Content Creator
We live in a digitally conscious world where most customers' wish lists are fed by what is trending rather than what they need. Before consumers buy a product, they consume it digitally, analyse the pros and cons of buying it, and then t ake that giant leap towards an investment. Like every other industry, the Automotive industry’s landscape is ever-evolving.
The current consumer pool is wide and catering to such an audience can sometimes be challenging. The automotive industry understands this and is ever-evolving to lure the man towards a machine and is trying, by all means, to make it his favourite toy.
This article highlights key consumer trends and the challenges in this industry and sums up the current business landscape.
The term second-hand has made way to pre-owned. Consumers prefer buying pre-owned cars that are less than four years old and are cheaper than their newer counterparts from registered dealers. The goal is to get the best of both worlds: the latest features at the best cost and condition. Led by this trend, the used car market is growing at a CAGR of 11% and reckons a sale of 8.3 million units by 2026.
What is there on the virtual medium is what a consumer wants now. They select a model, get virtual consultation and documentation and bring home their beast. Technology enablers like Roadster, G Forces, Digital Motors, Sophus3, and CitNow use AI and help automotive companies offer clients a larger-than-life online shopping experience. Apart from AI technology, compelling images, HD videos, and face-time help customers view their favourite machines virtually. Automotive companies, therefore, need to have a competitive digital marketing strategy on social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Youtube, and Twitter to capture the short attention spans of their audience.
Media plays a pivotal role in changing consumer mindset and creating a need that was not there already. Similarly, audio-video advertisements create compelling visuals and concepts to influence the market. For example, the latest BMW ad emphasises the accuracy of autonomous cars with an intelligent parking system. The increase in personal vehicles, a lack of parking spaces, and ads with such conviction lure customers into buying self-driven cars rather than normal ones. These cars also help improve fuel efficiency by 10% and reduce carbon emissions by 42 million metric tons yearly.
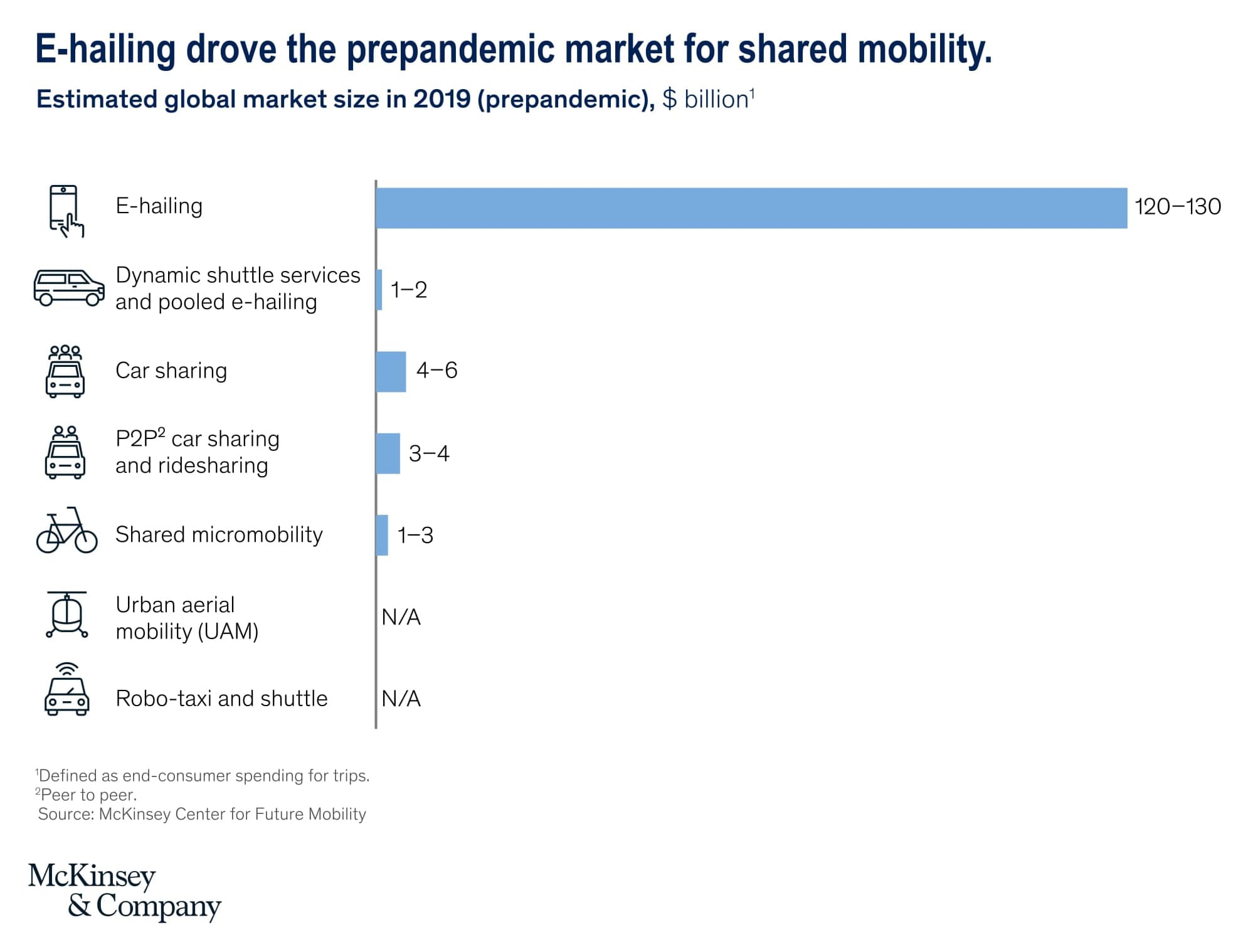
To address the rising transportation costs and reduce carbon emissions, a growing number of consumers show parity for shared mobility. Many companies apart from the key market players, uber and ola, are cropping up to facilitate this. This inclination can be a challenge for the Automotive sector, as it indicates a plunge in the purchase of new vehicle units to 2% growth per annum. Before the pandemic, commuters booked about 40 million shared trips to save time, and cost of commuting and to avoid parking woes. E-hailing accounts for up to $130 billion to $140 billion in global spending in 2019. During the pandemic with social distancing protocols, investments in shared mobility decreased radically. These have again surged after the pandemic eased out and seems to grow dramatically in 2022.
The need of the hour is the reduction of CO2 emissions and to comply with the 2C target set for 2030 as per the Paris Agreement. Electric vehicles must replace fossil-based ones and such a changed preference would radically transform the Automotive market. The fuel-based vehicles generate about 14% of the global CO2 emissions contributing to a high carbon footprint. Key players like Volkswagen have promised an investment of $35 billion to build electric vehicles to make 26 million EVS by 2030. Electric vehicles cause about 54% less CO2 emissions than fuel-based ones. Currently, there are more than 1.2 million EVS in the US to address the alarming global climate crisis.
The automotive industry faced insurmountable challenges during the pandemic and post-pandemic period. Two years down the recovery is still half-hearted and far from providing substantial relief.
During the first half of 2020, there was a low demand for vehicles putting a halt to the manufacturing of automobiles. The fear of the pandemic set people into fight or flight mode and survival was on top of their minds leading to huge losses. Though the latter half of 2020 saw a surge in demand, it is still way behind the previous demand benchmarks.
The plunging demand caused the industry to lay off labourers at an alarming rate. In India, about 0.34 million employees lost their jobs during the pandemic due to lesser demand for manufacturing and a production hiatus. Leading car manufacturer Volvo also announced their move to lay off 4100 highly paid and skilled workers. When the need for talented and experienced labourers rose again, the industry saw a workforce gap to meet its production demands.
The pandemic and geo-political upheaval disrupted the supply chain. China, the global manufacturing hub of automobiles, had to stop the export of two-thirds of its vehicle and auto parts production creating a series of setbacks for the automotive industry. The Russian-Ukrainian war also caused a spike in raw material costs leading to a dip in sales.
The shortage of semiconductors is one of the most profound effects of the pandemic challenging the automotive industry. During the pandemic, there was a high demand for semiconductors for use in computers, laptops, servers, 5G rollouts, and wireless communications. This demand in the IT world caused an evident shortage of chips required for the automotive industry. Demand for vehicles and chips increased during the later part of 2021 but the production of semiconductors was not enough to meet the rising demand.

From the above statistics, it is obvious that disruption in the supply chain of key importing countries can heavily impact business wealth. Due to the pandemic and the Russian-Ukrainian war, a series of blows hit the automotive industry causing heavy losses even for the key players. Volkswagen imported automotive parts from Ukraine and had to stop the production of assembly lines. Along similar lines, Hyundai’s and Toyota’s Petersburg plants, and Renault’s Moscow plant had to shut. The icing on the cake is the self-imposed ban by many countries on Russian exports. Therefore, there is an enormous deficit ($9.9 billion (up 39.7%)of imports VS export in Russia. Countries like Germany see a dip in GDP as their GDP is largely dependent on carmakers and their suppliers.
As told to CGTN by Ferdinand Dudenhoeffer, director of Germany’s CAR-Centre for Automotive Research, “The automotive industry will be the worst market in the world for the next ten years,”
These changes in trends and challenges have shaped the way the Automotive industry operates and paved a different path for it. Our next featured article highlights the future of the Automotive industry for the readers to understand the scope, opportunities, and inclination of the billion-dollar thriving market.
